William Huggins
| Sir William Huggins | |
|---|---|
Portrait by John Collier, 1905
|
|
| Born | February 7, 1824 Cornhill, Middlesex |
| Died | May 12, 1910 (aged 86) London, England |
| Nationality | British |
| Fields | astronomy |
| Known for | astronomical spectroscopy |
| Notable awards | Royal Medal (1866) Rumford Medal (1880) Copley Medal (1898) Henry Draper Medal (1901) Bruce Medal (1904) |
Sir William Huggins, OM, KCB, FRS (7 February 1824 – 12 May 1910) was an English amateur astronomer best known for his pioneering work in astronomical spectroscopy.
Contents |
Biography
William Huggins was born at Cornhill, Middlesex in 1824. He married Margaret Lindsay, daughter of John Murray of Dublin, who also had an interest in astronomy and scientific research.[1] She encouraged her husband's photography and helped to systemise their research.
Huggins built a private observatory at 90 Upper Tulse Hill, South London from where he and his wife carried out extensive observations of the spectral emission lines and absorption lines of various celestial objects. On August 29, 1864, Huggins was the first to take the spectrum of a planetary nebula when he analyzed NGC 6543.[2] He was also the first to distinguish between nebulae and galaxies by showing that some (like the Orion Nebula) had pure emission spectra characteristic of gas, while others like the Andromeda Galaxy had spectra characteristic of stars. Huggins was assisted in the analysis of spectra by his neighbour, the chemist William Allen Miller. Huggins was also the first to adopt dry plate photography in imaging astronomical objects.[1]
Huggins was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in June, 1865, was awarded their Royal Medal (1866), Rumford Medal (1880) and Copley Medal (1898) and delivered their Bakerian Lecture in 1885. He then served as their president from 1900 to 1905.
He died at his home in Tulse Hill, London after an operation in 1910 and was buried at Golders Green Cemetery.
Honours and awards
Awards
- Royal Medal (1866)
- Gold Medal of the Royal Astronomical Society (1867 with William Allen Miller, 1885)
- Rumford Medal (1880)
- Member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences (1883)
- Knight Commander of the Order of the Bath (1897)
- Copley Medal (1898)
- Henry Draper Medal from the National Academy of Sciences (1901)[3]
- Order of Merit (1902)
- Bruce Medal (1904)
Named after him
- Huggins (lunar crater)
- Huggins (Martian crater)
- Asteroid 2635 Huggins
Publications
- Spectrum analysis in its application to the heavenly bodies. Manchester, 1870 (Science lectures for the people; series 2, no. 3)
- (with Lady Huggins): An Atlas of Representative Stellar Spectra from
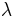 4870 to
4870 to 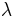 3300, together with a discussion of the evolution order of the stars, and the interpretation of their spectra; preceded by a short history of the observatory. London, 1899 (Publications of Sir William Huggins's Observatory; v. 1)
3300, together with a discussion of the evolution order of the stars, and the interpretation of their spectra; preceded by a short history of the observatory. London, 1899 (Publications of Sir William Huggins's Observatory; v. 1) - The Royal Society, or, Science in the state and in the schools. London, 1906.
- The Scientific Papers of Sir William Huggins; edited by Sir William and Lady Huggins. London, 1909 (Publications of Sir William Huggins's Observatory; v. 2)
See also
References
- ^ a b Becker, Barbara J., "Ch 4—1 - Margaret Huggins: The Myth of the 'able assistant'", Eclecticism, Opportunism, and the Evolution of a New Research Agenda: William and Margaret Huggins and the Origins of Astrophysics, https://eee.uci.edu/clients/bjbecker/huggins/ch4.html
- ^ Kwok, Sun (2000), "Chapter1: History and overview", The origin and evolution of planetary nebulae, Cambridge University Press, pp. 1–7, ISBN 0-521-62313-8, http://books.google.com/books?id=7NfqpZxO_o0C
- ^ "Henry Draper Medal". National Academy of Sciences. http://www.nasonline.org/site/PageServer?pagename=AWARDS_draper. Retrieved 19 February 2011.
External links
- Huggins, Sir William (1824–1910) Barbara J. Becker, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, 2004 (subscription required)
- Audio description of Huggins' work
- Eclecticism, Opportunism, and the Evolution of a New Research Agenda: William and Margaret Huggins and the Origins of Astrophysics Barbara J. Becker
|
|||||||||||